A child is considered to have urinary tract infection (UTI) when the urine of the child grows bacteria during a microbiological test and the amount is significantly high (more than one lakh per ml). During childhood 5% of girls and 2% of boys get UTI. In the new-born period more boys get UTI than girls. Among the girls half can get a second UTI within a year.
- Why is UTI important in children?
- How do we suspect urinary infection?
- How is UTI diagnosed?
- How is UTI managed?
- What is Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR)?
- How do we diagnose VUR?
- Can it be familial?
- What is the treatment for VUR?
- Is it safe to give a child long term antibiotics? Will it reduce the immunity?
- When is operation required for VUR? What does it involve?
- What are the other problems that might require operation?
- What are the general measures one should take to prevent urine infections?
Why is UTI important in children?
The incidence of underlying kidney problem is far higher in children compared to adults. 30-50% of children with UTI can have a kidney problem. If left untreated, they can lead to multiple infection, kidney scarring and in the long term hypertension and renal failure.
How do we suspect urinary infection?
When the UTI involves bladder alone, one experiences frequency, pain and burning sensation while passing urine. When the kidneys are also affected, high fever, vomiting, tummy pain and feeling unwell, can be the features.
How is UTI diagnosed?
Initial urine tests with microscope can help to identify presence of UTI. However it is confirmed only after growing organisms in a large number when tested in micro lab.
How is UTI managed?
After confirming the diagnosis, it is usually treated with a course of oral antibiotics. If kidney infection is suspected, the child may require hospitalization for IV fluids and antibiotics via IV route. Once UTI is treated, an ultrasound scan is requested to look for any underlying abnormalities.
What is Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR)?
In normal state, the urine travels in a one-way direction from kidneys to the bladder via the ureter. Once in bladder, the urine does not go back up either during storage or emptying. But in children with Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR), the urine goes upstream towards the kidneys. Because of this the kidneys are exposed to serious infection and scarring during any urinary infection.
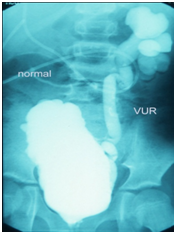
How do we diagnose VUR?
A test called MCU is done to diagnose VUR. In this a special radio opaque dye is injected via a catheter into the bladder. X-rays are taken while the child passes urine. Normally urine should not go up towards kidneys. But in children with VUR it goes up.
Can it be familial?
There is a slightly higher chance in future kids to have VUR when there is a kid with this problem in the family.
What is the treatment for VUR?
When VUR is present the usual treatment is to put them on long term low dose antibiotics (sometimes up to 4-5 years). This prevents the kidney getting infected. Most of them do not require surgery.
Is it safe to give a child long term antibiotics? Will it reduce the immunity?<
Long term antibiotics are only to protect kidneys. They are found to be safe and they do not cause reduction in immunity.
When is operation required for VUR? What does it involve?
When a child gets recurrent urine infections despite being on antibiotics, or when the reflux is very high grade with kidney scarring, then surgery is recommended. In this the length of ureter inside the bladder is increased, thereby creating a one-way valve. This prevents urine going back upstream. It is done under general anesthesia and involves 5-7 days hospital stay. The success rate is above 95%.
What are the other problems that might require operation?
In boys, circumcision has shown to reduce UTI significantly. If there is a blockage to the urinary tract, it will need correction. If urinary stones are present, they need to be removed. If there are congenital abnormalities of kidneys predisposing to UTI, they may need correction
What are the general measures one should take to prevent urine infections?
- Encourage your child to drink plenty of water
- Ask them to go to toilet regularly
- Prevent constipation by giving plenty of vegetables and fruits
- Avoid bladder irritants like coffee, tea and coke.
- Avoid exposing genitalia to soap, or shampoo, or bubble baths.
- Bio-yoghurts, curd etc have been shown to reduce UTI.
Key Points
- UTI in children need to be properly diagnosed and treated.
- Children are more likely to have underlying kidney abnormalities than adults.
- Some of them require surgery to prevent long term damage to the kidneys.


